An asteroid big enough to wipe out a city now has an increased chance of hitting Earth in seven years, NASA reported on Tuesday.
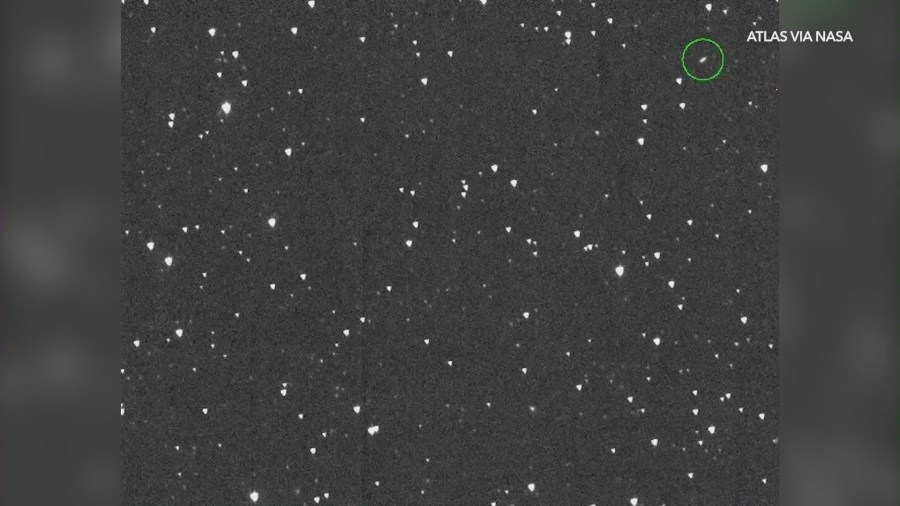
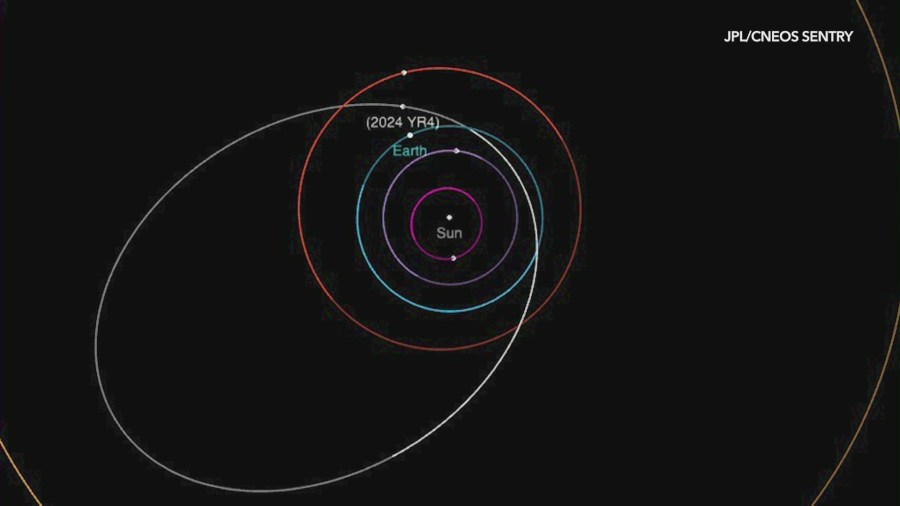
NASA first discovered the 130-to-300-foot-wide asteroid, named 2024 YR4, in December 2024, finding it only had a roughly 1% chance of impacting Earth on its trajectory.
Then, on Jan. 27, 2025, it surpassed a 1% chance of hitting Earth – an “important threshold,” according to NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
“ Currently, no other known large asteroids have an impact probability above 1%,” said NASA in a release.
However, the probability didn’t stop growing there. On Feb. 7, NASA issued an update saying the probability grew to 2.3% – but again, this was short-lived.
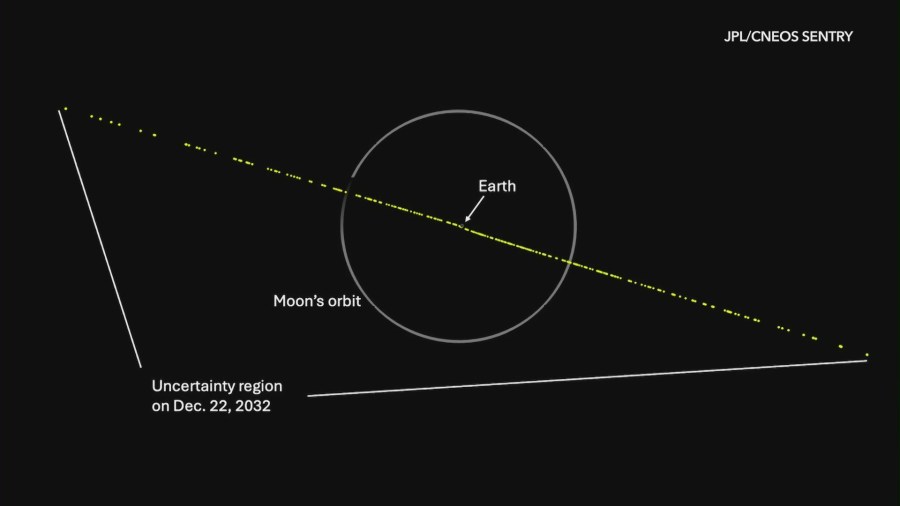
As of Feb. 18, there was a 3.1% chance that 2024 YR4 will impact Earth on Dec. 22, 2032.
This means the odds are now 1 in 32.
“It is possible that asteroid 2024 YR4 will be ruled out as an impact hazard, as has happened with many other objects that have previously appeared on NASA’s asteroid risk list, maintained by NASA’s Center for Near-Earth Object Studies,” NASA said in a release. “It is also possible its impact probability will continue to rise.”
While there is still a 96.9% chance that the asteroid will miss Earth, JPL said this rare asteroid has a significant risk – rating it at Torino Scale 3, which is uncommon.
JPL said this object is on the risk list because of how the impact probability has gradually increased during the months that have passed since discovering the asteroid’s existence.
“In the unlikely event that 2024 YR4 is on an impact trajectory, the impact would occur somewhere along a risk corridor which extends across the eastern Pacific Ocean, northern South America, the Atlantic Ocean, Africa, the Arabian Sea, and South Asia,” JPL said in a release.
NASA said its James Webb Space Telescope will observe the asteroid in March 2025 “to better assess the asteroid’s size.”
Scientists will continue observing 2024 YR4 while it’s still visible through April, but NASA said after then it will be too faint to observe until around June 2028.